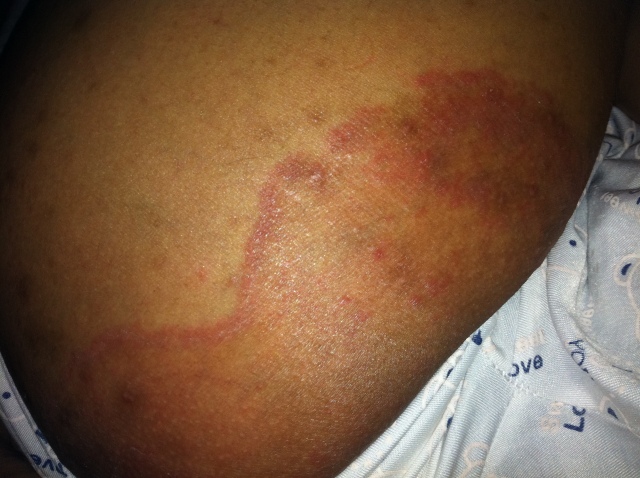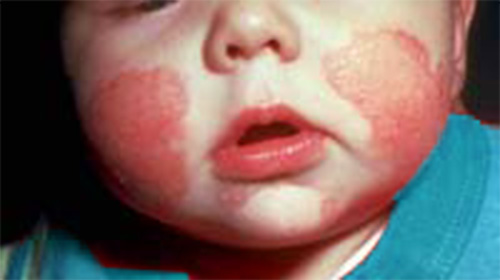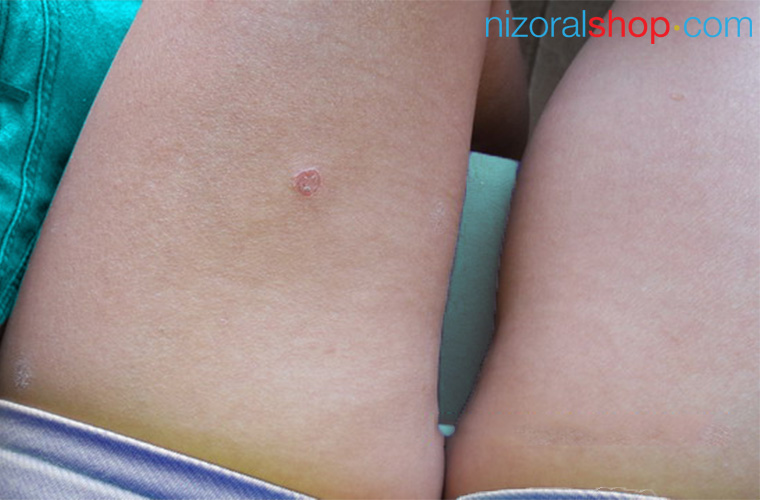
Person showing signs showing red, circular patches on their thigh
What Causes Red Circular Rashes?
Red, circular rashes can appear for many reasons. While they’re often harmless, they can signal an underlying skin condition.
Common Triggers
-
-
-
Dry Skin and Weather Changes
Cold, dry air or sudden temperature shifts can strip moisture from your skin, leading to flaky, coin-shaped patches. -
Harsh Soaps or Detergents
Chemicals in cleaning products or skincare can irritate sensitive skin, causing redness and itching. -
Allergies to Metals or Fabrics
Nickel jewelry or synthetic fabrics (like polyester) may trigger contact dermatitis, mimicking a circular rash.
-
-
Is It Ringworm or a Skin Rash? Key Differences
Many people mistake circular rashes for ringworm, but there are critical differences:
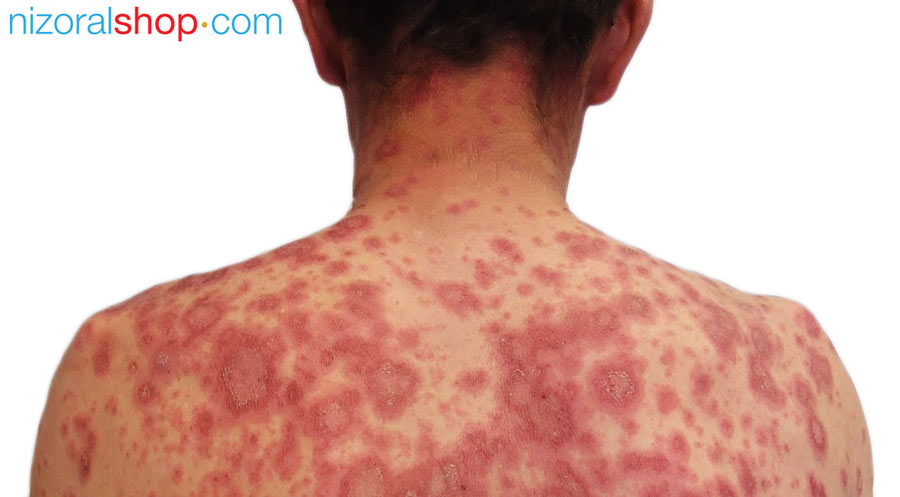
Woman showing symptoms of discoid eczema on back
How to Test for Ringworm at Home
Look for Scaling and Expansion
Ringworm spreads outward, creating a scaly, expanding ring. Circular rashes from eczema stay contained.
Try Moisturizing
If applying moisturizer reduces redness, it’s likely eczema, not ringworm (which requires antifungal cream).
How to Treat a Circular Rash on Arm, Leg, or Body
Step 1: Soothe the Itch Fast
Use Cold Compresses
Wrap ice in a cloth and hold it on the rash for 10 minutes to reduce inflammation.
Apply Fragrance-Free Moisturizer
Look for creams with ceramides (like CeraVe) to repair the skin barrier.
Step 2: Heal the Rash with Creams
Over-the-Counter Hydrocortisone
Use 1% hydrocortisone cream for mild itching and redness.
Ketoconazole Cream
For rashes linked to yeast or fungi, try Nizoral Cream (2% ketoconazole).
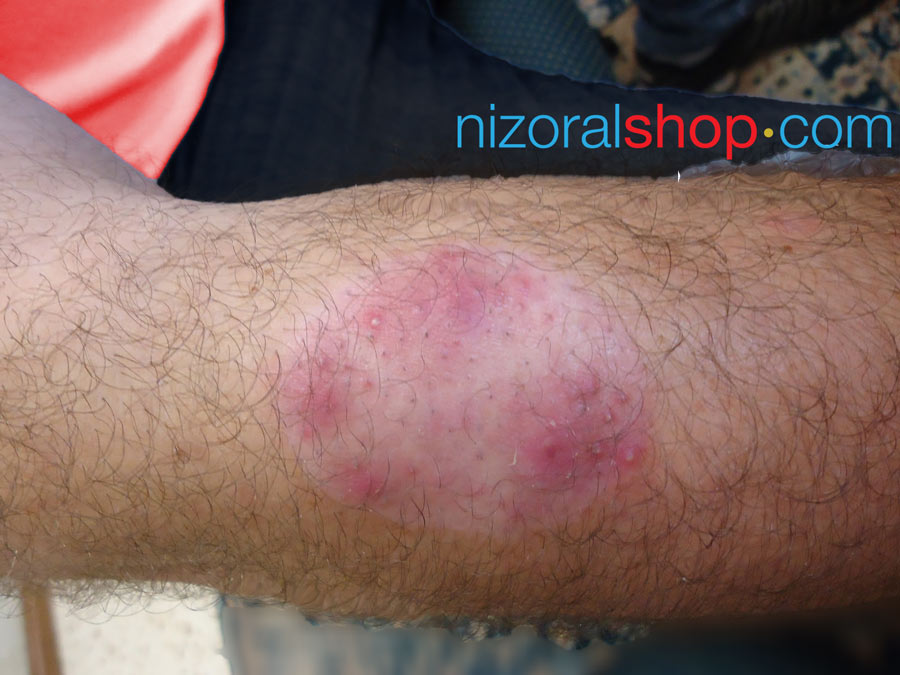
Man showing Nummular Eczema on his forearm
Natural Remedies for Itchy, Coin-Shaped Patches
Lavender Oil Bath for Dry, Scaly Patches
How to Use It:
Add 6–8 drops of lavender oil to a lukewarm bath and soak for 20 minutes to reduce dryness.
Diet Changes to Reduce Skin Inflammation
Elimination Diet Basics
Avoid common allergens like dairy, gluten, and peanuts for 4–6 weeks, then reintroduce them slowly.
When to See a Doctor for a Red Circular Rash
Signs of Infection
Pus, Swelling, or Fever
These symptoms require immediate medical care to prevent complications.
Prescription Treatments
Topical Steroids
For severe inflammation, doctors may prescribe stronger steroid creams.
FAQ: Your Top Questions Answered
Are Circular Rashes Contagious?
No – Unlike Ringworm
Discoid eczema isn’t contagious, so you don’t need to avoid close contact.
Can Stress Cause Red Circles on Skin?
Yes – Stress Weakens Skin
High stress levels can trigger flare-ups by compromising your skin’s protective barrier.
Key Takeaways
-
-
Red circular rashes are often linked to dryness, allergies, or eczema.
-
Moisturize daily to prevent flare-ups and reduce itching.
-
See a doctor if the rash spreads, oozes, or doesn’t improve in 2 weeks.
-
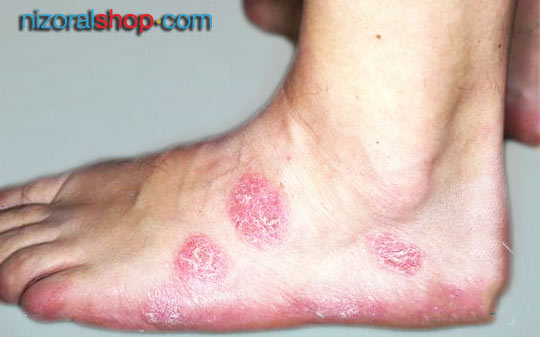
Patient suffering from foot nummular dermatitis
Check out our last news: Voltaren Side Effects
Related articles that may interest you:
Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. The material appearing on this page is for informational use only. It should not be used as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment.



.jpg)